Important Questions : Presentation of Data - Class 11 PDF Download
| Download, print and study this document offline |

Top Courses for Class 11
FAQs on Important Questions : Presentation of Data - Class 11
| 1. What is the purpose of data presentation in class 11? |
| 2. What are the different methods of data presentation in class 11? |
| 3. How can I choose the most appropriate method of data presentation for my class 11 project? |
| 4. What are the advantages of using visual aids for data presentation in class 11? |
| 5. How can I ensure the accuracy and reliability of data presentation in class 11? |
| Views | |
| Rating | |
| Last updated |
video lectures
Shortcuts and tricks, important questions : presentation of data - class 11, practice quizzes, study material, extra questions, viva questions, mock tests for examination, sample paper, objective type questions, past year papers, semester notes, previous year questions with solutions, important questions.

Important Questions : Presentation of Data Free PDF Download
Importance of important questions : presentation of data, important questions : presentation of data notes, important questions : presentation of data class 11, study important questions : presentation of data on the app.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.
- CBSE Class 11th
CBSE Presentation of Data Class 11 MCQs of Statistics for Economics Chapter 4
Presentation of data class 11 mcqs: find here multiple choice questions and answers for cbse class 11 statistics for economics chapter 4, presentation of data. these have been prepared as per cbse’s latest syllabus 2023-2024..

Presentation of Data Class 11 MCQs: This article consists of a list of 10 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) for CBSE Class 11 Statistics for Economics Chapter 4, Presentation of Data. Also, find attached a PDF download link for the same. Students don’t have to worry while referring to this list since they are completely based on the updated CBSE Syllabus 2023-2024 curriculum. They can use this list as a source of practice for the preparation of annual examinations.
- Easy form of assessment
- Less time consuming
- Tests in-depth knowledge
- Develops soft skills like brainstorming, problem-solving, critical thinking, and lateral thinking
- Covers multiple aspects of theory for assessment
- It can be easily analyzed
- On-the-spot feedback/result
- Mobile-friendly
Here, we have mentioned some of the most important benefits of MCQs. You can find many more such by actually involving in the process of solving MCQs. It is essential for students to practice MCQs and develop a habit of solving them within the deadlines, which happens to be the most critical task for students under pressure.
CBSE Class 11 Economics Syllabus 2023-2024
CBSE Class 11 Economics Deleted Syllabus 2023-2024(PDF)
Revision Notes for Class 11 Economics 2023-2024
MCQs for CBSE Class 11 Economics Collection of Data (2023-2024)
MCQs for CBSE Class 11 Economics Organization of Data (2023-2024)
MCQs for CBSE Class 11Economics Presentation of Data (2023-2024)
MCQs for CBSE Class 11 Statistics for Economics Chapter 4, Presentation of Data are presented below:
1. Which of the following is not a method of presenting data?
(a) Tabulation
(b) Diagrammatic representation
(c) Statistical analysis
(d) None of these
2. Which of the following is not a basis for the classification of a table?
(a)According to time
(b) According to space
(c) According to size
(d) According to the order
3. Which of the following is not a graphical method of presenting data?
(a) Bar diagram
(b) Pie chart
(c) Histogram
(d) Frequency polygon
4. Which of the following is not a limitation of tabulation?
(a) It is not suitable for large data sets.
(b) It is not suitable for comparing data sets.
(c) It is not suitable for presenting data in a clear and attractive manner.
5. Which of the following is not a limitation of diagrammatic representation?
(a) It is not suitable for presenting large data sets.
(d) It is not suitable for showing the relationship between different variables.
6. The number of rows in a table is known as the _______.
(d) Columns
7. The number of columns in a table is known as the _______.
(d) Rows
8. The title of a table is placed _______.
(a) Above the table
(b) Below the table
(c) In the middle of the table
9. The headings of the rows and columns of a table are called _______.
(a) Captions
(c) Subtitles
10. The data in a table is arranged in _______ order.
(a) Sequential
(b) Alphabetical
(c) Numerical
CBSE Class 11 Syllabus 2023-24 (All Subjects)
CBSE Class 11 Deleted Syllabus 2023-24 (All Subjects)
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification and articles in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari , Sarkari Result and Exam Preparation . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App .
- UP Police Answer Key 2024
- RRB NTPC Syllabus 2024
- RBI Grade B Admit Card 2024
- SSC GD Recruitment 2025
- SSC CGL Admit Card 2024
- UP Police Constable Question Paper 2024 PDF
- CDS Question Paper 2024
- RRB NTPC Recruitment 2024
- CBSE Class 12 Sample Papers 2024-25
- CBSE Class 10 Sample Papers 2024-25
- Education News
- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Class 11
- CBSE Class 11 Study Material
Latest Education News
Haryana Congress Candidates List: कांग्रेस 89 सीटों पर लड़ेगी चुनाव, 1 सीट CPM को, यहां देखें सभी के नाम
Haryana BJP Candidate List 2024: सभी 90 बीजेपी उम्मीदवारों की लिस्ट जारी, यहां देखें सभी के नाम
Sitaram Yechury Passes Away: वरिष्ठ वामपंथी नेता सीताराम येचुरी का निधन, पढ़ें उनके बारें में ये खास बातें
Find Out Which Political Leader's Body Donated to AIIMS
Asian Hockey Champions Trophy 2024: टीम इंडिया के मैचों की डिटेल्स, पॉइंट्स टेबल, और पूरा शेड्यूल यहां देखें
PM E-Drive Scheme Replaces FAME: No Incentive for E-Vehicles
Private Car Owners Won't Have to Pay Toll Tax Now, Only If...
EXIM Bank MT Recruitment 2024: Check Eligibility and How to Apply Here
GATE ME Previous Years Cut-off; Check Mechanical Engineering Past Years Qualifying Marks Trends
RSMSSB LDC Answer Key 2024 Released at rsmssb.rajasthan.gov.in: Download JA Question Paper PDF
CSIR NET Result 2024 OUT at csirnet.ntaonline.in: Download Marks Here
100+ GK Questions and Answers for Class 8
Hindi Diwas 2024: राष्ट्रीय और विश्व हिंदी दिवस में क्या है अंतर? पढ़ें यहां
भारत में कितनी है iPhone 16 सीरीज़ की कीमत? कब और कैसे खरीद सकते है, जानें यहां
Today Current Affairs One Liners 12 September 2024: Global Bio India 2024
Brain Teaser IQ Test: How Sharp Are Your Eyes? Spot the Odd Camel in 5 Seconds!
OPSC Civil Service Exam 2024 OUT at opsc.gov.in: Check Admit Card Date and Other Details
UP Police Constable Answer Key 2024 LIVE: 24 अगस्त शिफ्ट 1, 2 परीक्षा की उत्तर कुंजी जारी, ये रहा Link
RRB NTPC Mock Test 2024: Practice Online Test Series in English, Hindi and Other Languages
Current Affairs Quiz 12 September 2024: United Nations General Assembly 79th Session
NCERT solutions for Class 11 Economics (Statistics for Economics) chapter 4 - Presentation of Data [Latest edition]

Advertisements
Solutions for chapter 4: presentation of data.
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 4 of CBSE NCERT for Class 11 Economics (Statistics for Economics).
NCERT solutions for Class 11 Economics (Statistics for Economics) Chapter 4 Presentation of Data Exercise [Pages 56 - 57]
Answer the following questions, 1 to 10, choosing the correct answer..
Bar diagram is a ______
one-dimensional diagram
two-dimensional diagram
diagram with no dimension
none of the above
Data represented through a histogram can help in finding graphically the ______
all the above
Ogives can be helpful in locating graphically the ______
Data represented through arithmetic line graph help in understanding ______
long-term trend
cyclicity in data
seasonality in data
The width of bars in a bar diagram need not be equal.
The width of rectangles in a histogram should essentially be equal.
Histogram can only be formed with the continuous classification of data.
Histogram and column diagram is the same method of presentation of data.
The mode of a frequency distribution can be known graphically with the help of a histogram.
The median of a frequency distribution cannot be known from the ogives.
What kinds of diagrams are more effective in representing the following?
Monthly rainfall in a year
Composition of the population of Delhi by religion
Components of cost in a factory
Suppose you want to emphasize the increase in the share of urban non-workers and lower level of urbanization in India as shown in the Census of India, 2001. How would you do it in the tabular form?
How does the procedure of drawing a histogram differ when class intervals are unequal in comparison to equal class intervals in a frequency table?
The Indian Sugar Mills Association reported that ‘Sugar production during the first fortnight of December 2001 was about 3,87,000 tonnes, as against 3,78,000 tonnes during the same fortnight last year (2000). The off-take of sugar from factories during the first fortnight of December 2001 was 2,83,000 tonnes for internal consumption and 41,000 tonnes for exports as against 1,54,000 tonnes for internal consumption and nil for exports during the same fortnight last season.’
Present the data in tabular form.
Suppose you were to present these data in a diagrammatic form which of the diagrams would you use and why?
Present these data diagrammatically.
The following table shows the estimated sectoral real growth rates (percentage change over the previous year) in GDP at factor cost.
|
|
|
|
|
| 1994-95 | 5.0 | 9.2 | 7.0 |
| 1995-96 | -0.9 | 11.8 | 10.3 |
| 1996-97 | 9.6 | 6.0 | 7.1 |
| 1997-98 | -1.9 | 5.9 | 9.0 |
| 1998-99 | 7.2 | 4.0 | 8.3 |
| 1999-2000 | 0.8 | 6.9 | 8.2 |
Represent the data as multiple time-series graphs.
NCERT solutions for Class 11 Economics (Statistics for Economics) chapter 4 - Presentation of Data
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Class 11 Economics (Statistics for Economics) CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Class 11 Economics (Statistics for Economics) CBSE 4 (Presentation of Data) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Class 11 Economics (Statistics for Economics) chapter 4 Presentation of Data are Collection of Data, Sources of Data - Primary, Sources of Data - Secondary, Concepts of Sampling, How Basic Data is Collected, Methods of Collecting Data, Some Important Sources of Secondary Data, Organisation of Data, Meaning of Variables, Types of Variables, Organisation of Data - Raw Data, Organisation of Data - Frequency Series, Organisation of Data - Frequency Distribution, Tabular Presentation and Diagrammatic Presentation of Data - Geometric Form, Tabular Presentation and Diagrammatic Presentation of Data - Frequency Diagrams, Abular Presentation and Diagrammatic Presentation of Data - Arithmetic Line Graphs, Introduction to Presentation of Data, Textual Presentation of Data, Tabular Presentation of Data, Tabulation of Data and Parts of a Table, Diagrammatic Presentation of Data, Presentation of Data - Conclusion.
Using NCERT Class 11 Economics (Statistics for Economics) solutions Presentation of Data exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Class 11 Economics (Statistics for Economics) students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 4, Presentation of Data Class 11 Economics (Statistics for Economics) additional questions for Mathematics Class 11 Economics (Statistics for Economics) CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.

- Maharashtra Board Question Bank with Solutions (Official)
- Balbharati Solutions (Maharashtra)
- Samacheer Kalvi Solutions (Tamil Nadu)
- NCERT Solutions
- RD Sharma Solutions
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions
- TS Grewal Solutions
- ICSE Class 10 Solutions
- Selina ICSE Concise Solutions
- Frank ICSE Solutions
- ML Aggarwal Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science
- CBSE Study Material
- Maharashtra State Board Study Material
- Tamil Nadu State Board Study Material
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Study Material
- Mumbai University Engineering Study Material
- CBSE Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Arts
- CBSE Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Commerce
- CBSE Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Science
- CBSE Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 10
- Maharashtra State Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Arts
- Maharashtra State Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Commerce
- Maharashtra State Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Science
- Maharashtra State Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 10
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Arts
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Commerce
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Science
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 10
- Entrance Exams
- Video Tutorials
- Question Papers
- Question Bank Solutions
- Question Search (beta)
- More Quick Links
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Shaalaa App
- Ad-free Subscriptions
Select a course
- Class 1 - 4
- Class 5 - 8
- Class 9 - 10
- Class 11 - 12
- Search by Text or Image
- Textbook Solutions
- Study Material
- Remove All Ads
- Change mode
myCBSEguide
- Presentation of Data class...
- Presentation of Data class 11 Notes Economics
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
CBSE Economics Chapter 4 Presentation of Data class 11 Notes Economics in PDF are available for free download in myCBSEguide mobile app. The best app for CBSE students now provides Presentation of Data class 11 Notes Economics latest chapter wise notes for quick preparation of CBSE exams and school based annual examinations. Class 11 Economics notes on Chapter 4 Presentation of Data class 11 Notes Economics are also available for download in CBSE Guide website.
CBSE Guide Presentation of Data class 11 Notes
CBSE guide notes are the comprehensive notes which covers the latest syllabus of CBSE and NCERT. It includes all the topics given in NCERT class 11 Economics text book. Users can download CBSE guide quick revision notes from myCBSEguide mobile app and my CBSE guide website.
Download CBSE class 11th revision notes for Chapter 4 Presentation of Data class 11 Notes Economics in PDF format for free. Download revision notes for Presentation of Data class 11 Notes Economics and score high in exams. These are the Presentation of Data class 11 Notes Economics prepared by team of expert teachers. The revision notes help you revise the whole chapter in minutes. Revising notes in exam days is on of the best tips recommended by teachers during exam days.
Download Revision Notes as PDF
CBSE Class 11 Economics Revision Notes Chapter – 4 Presentation of Data class 11 Notes Economics
The presentation of data means exhibition of data in such a clear and attractive manner that these can be easily understood and analysed.
Forms of Presentation of data: 1. Textual/Descriptive Presentation 2. Tabular Presentation 3. Diagrammatic Presentation 4. Graphical Presentation
1. Textual/Descriptive Presentation of Data:- In this, data is presented in the form of text. This is suitable when quantity of data is not too large.
2. Tabulation – It is the process of presenting data in the form of a table. Parts or components of Table: 1. Table Number 2. Title 3. Caption Or Column Headings 4. Stubs Or Row Headings 5. Body of the Table 6. Unit of Measurement 7. Source 8. Head Note 9. Foot Note
Features of a good table: (a) Compatible with the objective (b) Helpful in comparison (c) Ideal Size (d) Stubs (e) Headings (f) Percentage and ratio (g) Sources of Data (h) Simplicity
Kinds of Table: 1. According to Purpose 2. According to originality 3. According to construction
Classification of tabular presentation of data 1. Qualitative Classification:- When classification is done according to attributes such as social status, nationality, etc. It is called qualitative classification. 2. Quantitative Classification:- In this, the data are classified on the basis of characteristics which are quantitative in nature. e.g., age, height, income, etc. 3. Temporal classification:- In this, time becomes the becomes the classifying variable and data are categorised according to time. Time may be in hours, weeks, years, etc. 4. Spatial classification:- When classification is done on the basis of place, it is called spatial classification. The place may be village, town, state, country, etc.
Diagrammatic Presentation : When data is presented in a simple and attractive manner in the form of diagrams is called diagrammatic presentation of data.
Types of Diagrammatic Presentation : 1. Geometric Form a. Pie Diagram b. Bar Diagram i. Simple ii. Multiple iii. Sub Divided iv. Percentage
2. Frequency Diagram a. Histogram b. Frequency Polygon c. Frequency Curve d. Ogive curve
3. Arithmetic Line Graph or Time series graph 1. Bar diagram:- Bar diagrams are those diagrams in which data are presented in the form of bars or rectangles. Simple bar diagram:- They are those diagrams which are based on a single set of numerical data. Different items are represented by different bars. Multiple bar diagram:- They are those diagrams which show two or more sets of data simultaneously. This type of diagram is, generally, used to make comparison between two sets of series. Sub divided bar diagram:- These are those diagrams which present simultaneously, total values and parts there in a set of a data. Percentage bar diagram:- They are those diagram which show simultaneously different parts off the values of a sets of data in terms of percentage. Deviation bar diagram:- These are used to compare the net deviation of related variables with respect to time and location. Bars which represent positive deviation and which represent negative deviation are drawn above and below the base line respectively. Pie or circular diagram is a circle divided into various segments showing the per cent values of a series. Histogram is graphical presentations of a frequency distribution of a continuous series.It can never be drawn for a discrete series. Frequency polygon is drawn by joining the mid points of the tops of rectangles in a histogram. It is constructed with the help of discrete as well as continuous series. Frequency curve is obtained by joining the points of a frequency polygon through free hand smooth curve not by straight lines. Cumulative frequency curves or ogive curve is the curve which is constructed by plotting cumulative frequency data on the graph paper in the form of a smooth curve. Arithmetic line Graphs or Time Series Graphs:- In this graph, time(hour,day, date, week, month, year) is plotted along X-axis and the corresponding value of variable along Y-axis.
Presentation of Data class 11 Notes
- CBSE Revision notes (PDF Download) Free
- CBSE Revision notes for Class 11 Economics PDF
- CBSE Revision notes Class 11 Economics – CBSE
- CBSE Revisions notes and Key Points Class 11 Economics
- Summary of the NCERT books all chapters in Economics class 11
- Short notes for CBSE class 11th Economics
- Key notes and chapter summary of Economics class 11
- Quick revision notes for CBSE exams
CBSE Class-11 Revision Notes and Key Points
Presentation of Data class 11 Notes Economics. CBSE quick revision note for class-11 Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry, Biology and other subject are very helpful to revise the whole syllabus during exam days. The revision notes covers all important formulas and concepts given in the chapter. Even if you wish to have an overview of a chapter, quick revision notes are here to do if for you. These notes will certainly save your time during stressful exam days.
- Revision Notes for class-11 Physics
- Revision Notes for class-11 Chemistry
- Revision Notes for class-11 Mathematics
- Revision Notes for class-11 Biology
- Revision Notes for class-11 Accountancy
- Revision Notes for class-11 Economics
- Revision Notes for class-11 Business Studies
- Revision Notes for class-11 Computer Science
- Revision Notes for class-11 Informatics Practices
- Revision Notes for class-11 Geography
To download Presentation of Data class 11 Notes, sample paper for class 11 Chemistry, Physics, Biology, History, Political Science, Economics, Geography, Computer Science, Home Science, Accountancy, Business Studies and Home Science; do check myCBSEguide app or website. myCBSEguide provides sample papers with solution, test papers for chapter-wise practice, NCERT solutions, NCERT Exemplar solutions, quick revision notes for ready reference, CBSE guess papers and CBSE important question papers. Sample Paper all are made available through the best app for CBSE students and myCBSEguide website.
- Introduction class 11 Notes Economics
- Collection of Data class 11 Notes Economics
- Organisation of Data class 11 Notes Economics
- Measures of Central Tendency class 11 Notes Economics
- Measures of Dispersion class 11 Notes Economics
- Correlation class 11 Notes Economics
- Introduction to Index Number class 11 Notes Economics
- Indian Economy on the Eve of Independence class 11 Notes Economics
- Indian Economy 1950-1990 class 11 Notes Economics
- Economic Reform Since 1991 class 11 Notes Economics
- Poverty class 11 Notes Economics
- Human Capital Formation in India class 11 Notes Economics
- Rural Development class 11 Notes Economics
- Employment : Growth, Informalisation and Other Issues class 11 Notes Economics
- Infrastructure class 11 Notes Economics
- Environment and Sustainable Development class 11 Notes Economics
- Inflation Problem and Policies class 11 Notes Economics
- Development Experience Of India a Comparison with Neighbours class 11 Notes Economics
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Food Security in India class 9 Notes Economics
- What is Democracy Why Democracy class 9 Notes Political Science
- Poverty as a Challenge class 9 Notes Economics
- The Story of Village Palampur class 9 Notes Economics
- People as Resource class 9 Notes Economics
- Inflation Problem and Policies Class 12 Notes Economics
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
Statistics for Economics Class 11 Notes Chapter 4 Presentation of Data
July 5, 2019 by Sastry CBSE
Textual Presentation In textual presentation, data are a part of the text of study or a part of the description of the subject matter of study.
Tabular Presentation of Data “Tabulation involves the orderly and systematic presentation of numerical data in a form designed to elucidate the problem under consideration”
Components of a Table Following are the principal components of a table
- Table number
- Body or field
Classification of Data and Tabular Presentation (i) Qualitative Classification of Data and Tabular Presentation Qualitative classification occurs when data are classified on the basis of qualitative attributes or qualitative.
(ii) Characteristics of a Phenomenon
- Quantitative Classification of Data These occurs when data are classified on the basis ot quantitative characteristics of a phenomenon.
- Temporal Classified of Data In this, data are classified according to time, and time becomes the classifying variable.
(iii) Spatial Classification In spatial classification place, location becomes the classifying variable. It may be a village, a town, a district, etc. (iv) Merits of Tabular Presentation
- Simple and brief presentation
- Facilitates comparison
- Easy analysis
- High lights characteristics of data
Diagrammatic Presentation of Data These translates quite effectively the highly abstract ideas contained in numbers into more concrete and easily comprehensible form. Diagrammatic presentation is classified as given below (i) Bar Diagrams Bar diagrams are these diagrams in which data are presented in the form of bars or rectangles. Types of Bar Diagram are as follows
- Simple Bar Diagrams Simple bar diagrams are those diagrams which are based on a single set of numerical data.
- Multiple Bar Diagrams These are those diagram which show two or more sets of data simultaneously.
- Sub Divided Bar Diagram Sub-divided bar diagram are those diagrams which simultaneously present total values as well as part values of a set of data.
- Percentage Bar Diagram Percentage bar diagrams are those diagrams which show simultaneously, different parts of the values of a set of data in terms of percentages.
(ii) Pie or Circular Diagrams Pie diagram is a circle divided into various segments showing the per cent values of a series. This diagram does not show absolute values. (iii) Frequency Diagram Data in the form of grouped frequency distributions are generally represented by frequency diagram like histogram, frequency polygon, frequency curve and ogive.
- Histogram of equal class intervals
- Histogram of unequal class intervals
- Polygon Polygon is another form of diagrammatic presentation of data. It is formed by joining mid points of the tops of all rectangles in a histogram. However, a polygon can be drawn even without constructing a histogram.
- Frequency Curve A frequency curve is a curve which is plotted by joining the mid points of all tops of histogram by free hand smoothed curves and not by straight lines.
- Less than Method In this method, beginning from upper limit of the 1st values we go on adding the frequencies corresponding to every next upper limit of the series.
- More than Method In this method, we take cumulative total of the frequencies beginning with lower limit of the 1st class interval.
(iv) Arithmetic Line Graph An arithmetic line graph is also called time series graph. In it time is plotted along x-axis and the value of the variable along y-axis. A line graph by joining these plotted points, these obtained is called time series graph.
Rules for Constructing a Graph
- Choice of scale
- Proportion of axis
- Method of plotting the points
- Lines of different types
- Table of data
- Use of false line
- One Variable Graph One variable graph are those graphs in which values of only one variable are shown with respect to some time period.
- Two or More than Two Variable Graphs These – are the graphs in which values of two variables are simultaneously shown with respect to some period of time.
Merits of Diagrammatic and Graphic Presentation
- Simple and understandable information
- Lasting impact
- No need of training or specialised knowledge
- Attractive and effective means of presentation
- A quick comparative glance
- Information and entertaining
- Location of averages
- Study of correlation
Limitations of Diagrammatic and Graphic Presentation
- Limited use
- Only preliminary conclusions
Statistics for Economics Class 11 Notes
Class 11 economics notes, free resources.
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Presentation of Data Class 11 Statistics Notes And Questions
Please refer to Presentation of Data Class 11 Statistics notes and questions with solutions below. These Class 11 Statistics revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Statistics books for Class 11. You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 11 Statistics Presentation of Data Notes and Questions
The presentation of data means exhibition of the data in such a dear and attractive manner that these are easily understood and analysed. There are many forms of presentation of data of which the following three are well known: (i) Textual or Descriptive Presentation, (ii) Tabular Presentation, and (iii) Diagrammatic Presentation. The present chapter focuses on Textual and Tabular Presentation of data. Diagrammatic Presentation of data is discussed in the next chapter.
1. TEXTUAL PRESENTATION In textual presentation, data are a part of the text of study or a part of the description of the subject matter of study. Such a presentation is also called descriptive presentation of data. This is the most common form of data presentation when the quantity of data is not very large. Here are some examples:
Example 1 In a strike call given by the trade unions of shoe making industry in the city of Delhi, 50% of the workers reported for the duty, and only 2 out of the 20 industries in the city were totally closed.
Example 2 Surveys conducted by a Non-government Organisation reveal that, in the state of Punjab, area under pulses has tended to shrink by 40% while the area under rice and wheat has tended to expand by 20%, between the years 2001-2011.
Suitability Textual presentation of data is most suitable when the quantum of data is not very large. A small volume of data presented as a part of the subject matter of study becomes a useful supportive evidence to the text. Thus, rather than saying that price of gold is skyrocketing, a statement like price of gold has risen by 50% during the financial year 2017- 18 is much more meaningful and precise. One need not support the text with voluminous data in the form of tables or diagram when the textual matter itself is very small and includes only a few observations. Indeed, textual presentation of data is an integral component of a small quantitative description of a phenomenon. It gives an emphasis of statistical truth to the otherwise qualitative observations.
Drawbacks A serious drawback of die textual presentation of data is that one has to go through the entire text before quantitative facts about a phenomenon become evident. A picture or a set of bars showing increase in the price of gold during a specified period is certainly quite informative even on a casual glance of the reader. Textual presentation of data, on the other hand, does not offer anything to the reader at a mere glance of the text matter. The reader must read and comprehend (he entire text. When the subject under study is vast and involves comparison across different areas/countries, textual presentation of data would only add to discomfort of the reader.
2. TABULAR PRESENTATION In the words of Neiswanger, “A statistical table is a systematic organisation of data in columns and rows” Vertical dissections of table (||) are known as columns and horizontal dissections (=) are known as rows.
Tabulation is the process of presenting data in the form of a table. According to Prof. L.R. Connor, ‘tabulation involves the orderly and systematic presentation of numerical data in a form designed to elucidate the problem under consideration. ”
In the words of Prof. M.M. Blair, “Tabulation in its broadest sense is an orderly arrangement of data in columns and rows.”
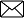
Components of a Table Following are the principal components of a table:
(1) Table Number: First of all, a table must be numbered. Different tables must have different numbers, e.g., 1, 2, 3, etc. These numbers must be in the same order as the tables. Numbers facilitate location of the tables.
(2) Title: A table must have a title. Title must be written in bold letters. It should attract the attention of the readers. The title must be simple, clear and short. A good title must reveal: (i) the problem under consideration, (ii) the time period of the study, (iii) the place of study, and (iv) the nature of classification of data. A good title is short but complete in all respects.
(3) Head Note: If the title of the table does not give complete information, it is supplemented with a head note. Head note completes the information in the title of the table. Thus, units of the data are generally expressed in the form of lakhs, tonnes, etc. and preferably in brackets as a head-note.
(4) Stubs: Stubs are titles of the rows of a table. These titles indicate information contained in the rows of the table.
(5) Caption: Caption is the title given to the columns of a table. A caption indicates information contained in the columns of the table. A caption may have sub-heads when information contained in the columns is divided in more than one class. For example, a caption of ‘Students’ may have boys and girls as sub-heads.
(6) Body or Field: Body of a table means sum total of the items in the table. Thus, body is the most important part of a table. It indicates values of the various items in the table. Each item in the body is called ‘cell’.
(7) Footnotes: Footnotes are given for clarification of the reader. These are generally given when information in the table need to be supplemented. «
(8) Source: When tables are based on secondary data, source of the data is to be given. Source of the data is specified below the footnote. It should give: name of the publication and publisher, year of publication, reference, page number, etc.
Difference between Table and Tabulation
While tabulation refers to the method or process of presenting data in the form of rows and columns, table refers to the actual presentation of data in the form of rows and columns. Table is the consequence (result) of tabulation.
Check [he following format of a table showing its various components:
Guidelines for the Construction of a Table or Features of a Good Table
Construction of a table depends upon the objective of study. It also depends upon the wisdom of the statistician. There are no hard and fast rules for the construction of a table. However, some important guidelines should be kept in mind. These guidelines are features of a good table. These are as under:
(1) Compatible Title: Title of a table must be compatible with the objective of the study. The title should be placed at the top centre of the table.
(2) Comparison: It should be kept in mind that items (cells) which are to be compared with each other are placed in columns or rows close to each other. This facilitates comparison.
(3) Special Emphasis: Some items in the table may need special emphasis. Such items should be placed in the head rows (top above) or head columns (extreme left). Moreover, such items should be presented in bold figures.
(4) Ideal Size: Table must be of an ideal size. To determine an ideal size of a table, a rough draft or sketch must be drawn. Rough draft will give an idea as to how many rows and columns should be drawn for presentation of the data.
(5) Stubs: If rows are very long, stubs may be given at the right hand side of the table also.
(6) Use of Zero: Zero should be used only to indicate the quantity of a variable. It should not be used to indicate the non-availability of data. If the data are not available, it should be indicated by ‘n.a.’ or (-) hyphen sign.
(7) Headings: Headings should generally be written in the singular form. For example, in the columns indicating goods, the word ‘good’ should be used.
(8) Abbreviations: Use of abbreviations should be avoided in the headings or subheadings of the table. Short forms of the words such as Govt., m.p. (monetary policy), etc. should not be used. Also such signs as “(ditto)” should not be used in the body of the table.
(9) Footnote: Footnote should be given only if needed. However, if footnote is to be given, it must bear some asterisk mark (*) corresponding to the concerned item. (10) Units: Units used must be specified above the columns. If figures are very large, units may be noted in the short form as ‘000’ hectare or ‘000’ tonnes.
(11) Total: In the table, sub-totals of the items must be given at the end of each row. Grand total of the items must also be noted.
(12) Percentage and Ratio: Percentage figures should be provided in the table, if possible. This makes the data more informative.
(13) Extent of Approximation: If some approximate figures have been used in the table, the extent of approximation must be noted. This may be indicated at the top of the table as a part of head note or at the foot of the table as a footnote.
(14) Source of Data: Source of data must be noted at the foot of the table. It is generally noted next to the footnote.
(15) Size of Columns: Size of the columns must be uniform and symmetrical.
(16) Ruling of Columns: Columns may be divided into different sections according to similarities of the data.
(17) Simple, Economical and Attractive: A table must be simple, attractive and economical in space.
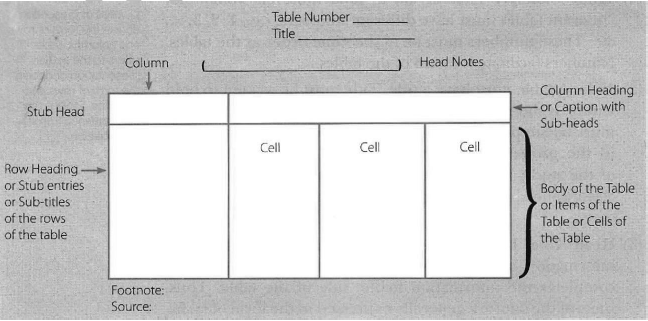
Kinds of Tables There are three basis of classifying tables, viz., (1) purpose of a table, (2) originality of a table, and (3) construction of a table. According to each of these bases, statisticians have classified tables as in the following flow chart:
Let us attempt a brief description of the various kinds of tables:
(1) Tables according to Purpose
According to purpose, there are two kinds of tables:
(i) General Purpose Table: General purpose table is that table which is of general use. It does not serve any specific purpose or specific problem under consideration. Such tables are just ‘data bank’ for the use of researchers for their various studies. These tables are generally attached to some official reports, like Census Reports oflndia. These are also called Reference Tables.
(ii) Special Purpose Table: Special purpose table is that table which is prepared with some specific purpose in mind. Generally, these are small tables limited to the problem under consideration. In these tables data are presented in the form of result of the analysis. That is why these tables are also called summary tables.
(2) Tables according to Originality On the basis of originality, tables are of two kinds: (i) Original Table: An original table is that in which data are presented in the same form and manner in which they are collected. (ii) Derived Table: A derived table is that in which data are not presented in the form or manner in which these are collected. Instead the data are first converted into ratios or percentage and then presented.
(3) Tables according to Construction
According to construction, tables are of two kinds:
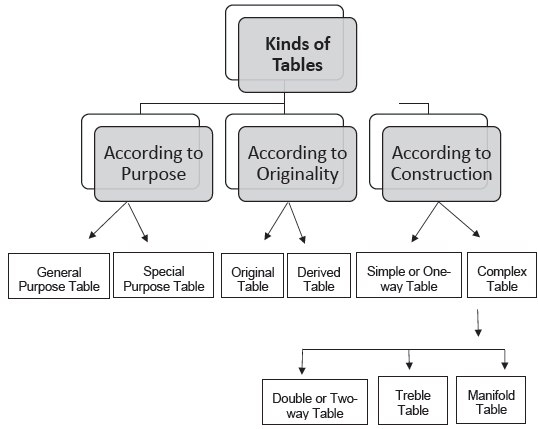
(i) Simple or One-way Table: A simple table is that which shows only one characteristic of the data. Table 2 below is an example of a simple table. It shows number of students in a college:
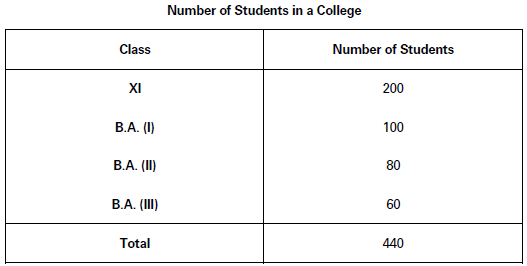
(ii) Complex Table: A complex table is one which shows more than one characteristic of the data. On the basis of the characteristics shown, these tables may be further classified as:
(a) Double or Two-way Table: A two-way table is that which shows two characteristics of the data. For example, Table 3, showing the number of students in different classes according to their sex, is a two-way table: Number of Students in a College (According to Sex and Class)
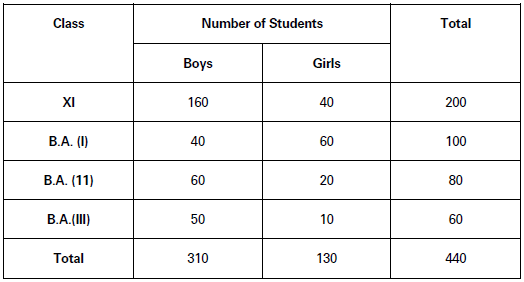
(b) Treble Table: A treble table is that which shows three characteristics of the data. For example, Table 4 shows number of students in a college according to class, sex and habitation. Number of Students in a College (According to Class, Sex and Habitation)
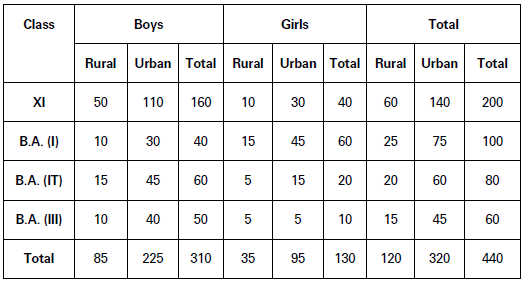
(c) Manifold Table: A manifold table is the one which shows more than three characteristics of the data. Table 5, for example, shows number of students in a college according to their sex, class, habitation and marital status. Number of Students in a College (According to their Sex, Class, Habitation and Marital Status)
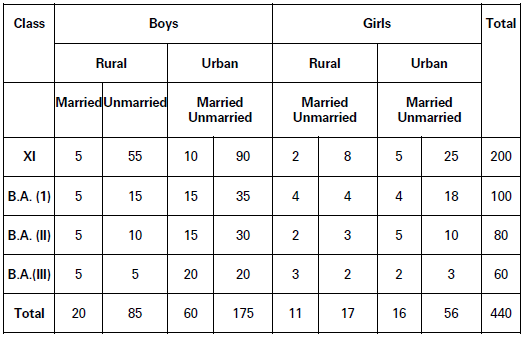
Classification of Data and Tabular Presentation Tabular presentation is based on four-fold classification of data, viz., qualitative, quantitative, temporal, and spatial. Following are the details with suitable illustrations.
(1) Qualitative Classification of Data and Tabular Presentation: Qualitative classification occurs when data are classified on the basis of qualitative attributes or qualitative characteristics of a phenomenon. Example: Data of unemployment may relate to rural-urban areas, skilled and unskilled workers, or male and female job-seekers. Table 6 below is an example of tabular presentation of data when data are classified on the basis of qualitative attributes or qualitative characteristics.

(This is an imaginary table. In this table, male and female are such characteristics/attributes which are qualitative and cannot be quantified.)
(2) Quantitative Classification of Data and Tabular Presentation: Quantitative classification occurs when data are classified on the basis of quantitative characteristics of a phenomenon.
Example: Data on marks in Mathematics by the students of Class XII in CBSE examination. Table 7 shows tabular presentation of data when data are classified on the basis of quantitative characteristics.
Marks Obtained by Students of Class XII of XYZ School
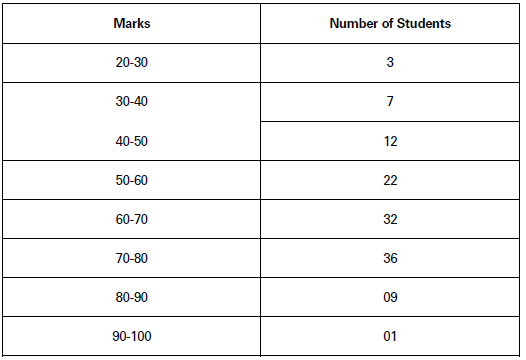
Source: Result Sheets Here, marks are a quantifiable variable and data are classified in terms of different class intervals of marks.
(3) Temporal Classification of Data and Tabular Presentation:
In temporal classification, data are classified according to time, and time becomes the classifying variable.
Example: Sale of Cell phones in different years during the period 2014-2018 in the city of Delhi. Table 8 shows tabular presentation of data on the basis of temporal classification.
Annual Sale of Cell Phones in the City of Delhi (2014-2018)
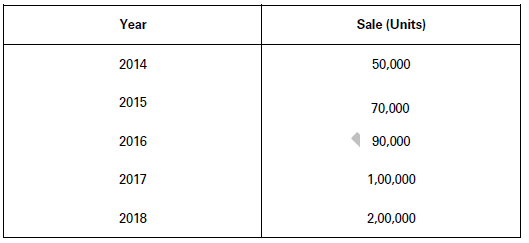
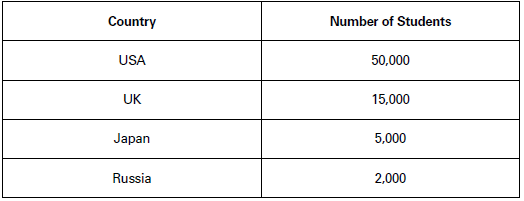
(4) Spatial Classification : In spatial classification, place/location becomes the classifying variable. It may be a village, a town, a district, a state or a country as a whole. Example: Number of Indian students studying in different countries of the world during a particular year. Table 9 is an example of tabular presentation based on spatial classification of data.
Indian Students in different Countries of the World (2018)
Merits of Tabular Presentation Following are the principal merits of tabular presentation of data:
(1) Simple and Brief Presentation: Tabular presentation is perhaps the most simplest form of data presentation. Data, therefore, are easily understood. Also, a large volume of statistical data is presented in a very brief form.
(2) Facilitates Comparison: The tabulation facilitates comparison of data by presenting the data in different classes.
(3) Easy Analysis: It is very easy to analyse the data from tables. It is by organising the data in the form of table that one finds out their central tendency, dispersion and correlation.
(4) Highlights Characteristics of Data: Tabulation highlights characteristics of data. Accordingly, it becomes easy to remember the statistical facts.
(5) Economical: Tabular presentation is a very economical mode of data presentation. It saves time as well as space.

Related Posts

Class 11 Physical Education Notes And Questions

Class 11 Economics Notes and Questions

International Business Class 11 Business Studies Notes And Questions

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- Toppers Notes
- Most Repeated Question
- Diagram Based Question
- Study Planner
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- BCECE Previous Year Paper
- JCECE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Important Question
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- MBA General Knowledge
- CAT Mind Map
- CAT Study Planner
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Class 11 Solutions TR Jain (PDF Available)
While preparing for the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams, it is very normal to get distracted. Students can avoid being distracted by solving plenty of questions from the Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams class 11 solutions TR Jain; they can automatically build a strong foundation of the chapter. A strong foundation in Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams can be useful in completing further chapters in the class 11 Economics syllabus.
Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams Class 11 Solutions TR Jain PDF
The Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams class 11 solutions TR Jain PDF is considered to be versatile in nature: it can be adapted easily by students. This type of nature can help students to start practising questions of the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams and can also refer to answers. Practising questions of the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams can help students to understand the concepts in a proper way.
Where Can You Find a Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams Class 11 Solutions TR Jain?
Students can find the Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams class 11 solutions TR Jain on the Selfstudys website by following the given steps:
- Visit the Selfstudys website.
- Bring the arrow towards the Books & Solutions from the navigation bar/ button.
- A drop down menu will appear, select TR Jain from the given list.
- A new page will appear, select class 11th and then click the Economics- TR Jain Solution .
- Again a new page will appear, select the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams from the list of chapters.
Features of Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams Class 11 Solutions TR Jain
The features of Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams class 11 solutions TR Jain are considered to be distinctive trait which can be helpful to many students as well as teachers to go through the answers, those features are:
- Available in the PDF: The TR Jain class 11 solutions of Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams in the PDF are considered to be digital papers which are quicker and easier to read.
- Simplified Format: Answers of all questions of the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams are explained in a stepwise manner so that students can have a good understanding of all concepts and topics.
- According to Exam Syllabus: Questions in the class 11 TR Jain solutions of the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams are arranged according to the exam syllabus so that students can enhance their knowledge regarding the topics and concepts.
- Different Types of Questions are Asked: In the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams which is given in the TR Jain class 11 solutions book, different types of questions are asked: tick the appropriate answers, true or false, numerical based questions, etc. By practising different types of questions from the given book, students can have a major impact on the preparation of the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams.
- All Topics are Covered: Questions asked are according to the topics covered in the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams, accordingly students can develop their knowledge.
- Available Free of Cost: The questions of the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams are generally considered to be free of cost that there is no need to pay any kind of amount to have an access to it.
Benefits of Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams Class 11 Solutions TR Jain
Students can be benefited a lot by practising questions from the Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams class 11 solutions TR Jain because of these reasons:
- Gives an Insight to Types of Questions: No matter what type of exam a student is attending but it is important for students to have an insight into all types of questions; same is followed while preparing the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams. Students can easily get to know about the questions of the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams with the help of class 11 TR Jain book.
- Acts as Revision Tool: The TR Jain class 11 book can be considered as a gold mine for students who want to revise the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams as the book follows the same format as the actual class 11 final exam.
- Teaches About Time Management: It is quite common among students to manage their time while attempting questions of the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams; they can learn the skill with the help of class 11 TR Jain solutions.
- Helps to Understand the Basic Structure of the Chapter: It is very important for students to know the basic structure for the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams then only they can score well in those questions; they can easily know the structure with the help of class 11 TR Jain book.
- Can Save Time: It is important for students to utilise their time in completing the concepts and practising questions and not in searching for solutions; they can save their time with the help of Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams class 11 solutions TR Jain.
- Improves the Motivation: It is a must for students to be motivated throughout the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams preparation; this can be maintained by practising a lot of questions from the TR Jain class 11 book and Solutions available at Selfstudys.

How to Utilise the Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams Class 11 Solutions TR Jain Effectively?
The main problem among students is that they don’t know how to utilise the Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams class 11 solutions TR Jain in an effective way, below are some guidelines that a student can follow:
- To Practise More: Students can utilise the class 11 solutions of TR Jain to practise several questions and can understand the concepts in a better way.
- To Understand Topics Clearly: It is important for students to have a better and accurate understanding of Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams topics, for that they can use the TR Jain class 11 book.
- To Score High: There are a number of tricks that students follow to improve the chances of getting higher marks in the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams; the best trick is to use the reference book of class 11 TR Jain along with solutions.
- To Summarise and Revise Topics: During preparation, it is important for students to summarise all the topics of Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams; they can easily revise with the help of class 11 solutions of TR Jain.
- To Stay Focused: As we all know that it is important for students to stay focused while preparing for Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams; they can improvise their attention span by practising questions from class 11 TR Jain Solutions.
The Impact of a Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams Class 11 Solutions TR Jain in the Preparation?
Students can automatically have a major impact on their economics preparation by using the Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams class 11 solutions TR Jain, some of the positive impact are discussed below:
- Provides Crisp and Concise Content: Topics and questions of the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams are provided in a crisp and concise manner so that students can understand complex parts too.
- Can Prepare for Exams: These solutions of Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams in the TR Jain book are designed in such a way that students can easily prepare for the final exam.
- Can Have a Practical Knowledge: By practising questions of Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams from the TR Jain class 11 book, students can attain practical knowledge of the chapter. Similarly, using the solutions of TR Jain Class 11 helps cross-checking the answers which eventually boost the practical knowledge.
- Can Analyse Solutions: Students can easily match the given answers after attempting questions of Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams with the help of solutions provided in the TR Jain class 11 PDF Solutions, this is considered to be the major impact in the preparation level.
- Can Improvise Concentration: Concentration is a term in which a person is present mentally and physically to complete the task; students can improve their concentration by practising questions from the Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams Class 11 Solutions of TR Jain.
When Is the Best Time to Utilise a Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams Class 11 Solutions TR Jain?
During preparation, it is very important for students to utilise the Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams class 11 solutions TR Jain, accordingly they can score well, but it is important for them to practise in a specific time which is given below:
- To Improve Comprehension: It is important for students to write answers for each question of the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams according to the marks given; so it is best to utilise the class 11 TR Jain book.
- To Develop Knowledge: Students can utilise the class 11 TR Jain book to develop their knowledge regarding the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams. This developed knowledge can help students to score well in those questions which is related to the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams.
- After Each Concept: Students can start solving questions from the class 11 TR Jain book after completing each concept of the chapter Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams; accordingly students can improvise their knowledge about the particular concept referring to the TR Jain Class 11 Economics Solutions of Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams.
- After Completing the Chapter: Students can take the help of Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams class 11 solutions of TR Jain book after completing the chapter so that they can understand the topics then and there.
- To Find Answers: After attempting questions of Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams, it is a must to refer to answers; students can find answers from the class 11 book of TR Jain that we provide here at Selfstudys.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

Presentation of Data Class 11 Notes and Mind map
- Download file
Welcome to WitKnowLearn, where we offer a comprehensive guide to the 'Presentation of Data' in Class 11, a pivotal topic in the NCERT Class 11 Economics curriculum. Our expertly crafted Presentation of Data Class 11 Notes are designed to provide students with a clear and thorough understanding of this essential subject.
Presentation of data is a vital skill in Class 11 Economics, as it enables students to effectively communicate statistical information. Our notes cover everything from basic presentation methods to advanced diagrammatic techniques. We delve deep into different ways of presenting data, ensuring that you grasp both the theory and application of these methods.
To complement our notes, we've developed a unique Presentation of Data Class 11 Mind Map. This innovative tool simplifies complex concepts and visually connects various ideas related to data presentation. It’s an excellent resource for quick revision and helps solidify your understanding of the topic.
Moreover, we offer a variety of Presentation of Data Class 11 Extra Questions and Answers to challenge and test your knowledge. These questions are specifically designed to prepare you for your exams, covering all the essential aspects of data presentation.
For students looking for an in-depth understanding of diagrammatic presentation, our Diagrammatic Presentation of Data Class 11 Notes are just what you need. These notes provide detailed insights into different types of diagrams and how they can be used to represent data effectively.
At WitKnowLearn, we are dedicated to making learning engaging and accessible. Dive into our resources for Presentation of Data in Class 11 and master the art of communicating data with clarity and precision. Get ready to excel in your Class 11 Economics with WitKnowLearn!
Presentation of Data Class 11
In Class 11, the presentation of data is a crucial skill, integral to understanding and communicating statistical information effectively. This topic equips students with the ability to visually represent data, making complex information easily understandable.
The presentation of data includes various methods such as tables, charts, graphs, and diagrams. Students learn to choose the appropriate method based on the type of data and the intended audience. This skill is not just academic; it has practical applications in various fields like economics, business, and social sciences. Mastery of data presentation is essential for students to accurately interpret data, draw meaningful conclusions, and make informed decisions.
Presentation of Data Class 11 Notes
Our comprehensive notes on the presentation of data for Class 11 provide a detailed exploration of various data presentation techniques. These notes cover the fundamentals of organizing data in tables, creating different types of charts and graphs like bar graphs, histograms, pie charts, and line graphs. Each method is explained with its specific usage, advantages, and limitations.
The notes also delve into more complex forms of data presentation, such as frequency polygons and ogives. Through these notes, students gain a thorough understanding of how to present data in the most effective way, enhancing their analytical and interpretive skills.
Presentation of Data Class 11 Mind Map
The Presentation of Data Class 11 Mind Map is an innovative learning tool that visually organizes key concepts and methods related to data presentation. This mind map includes branches for different types of data presentation techniques, highlighting their uses and characteristics. It serves as an excellent revision tool, helping students quickly recall and connect various aspects of data presentation.
The mind map simplifies complex information, making it easier for students to grasp and retain the material for their exams and practical applications.
Presentation of Data Class 11 Extra Questions Answers
To reinforce learning, our Presentation of Data Class 11 Extra Questions and Answers are an invaluable resource. These questions cover a wide range of topics, from basic understanding to application-based scenarios. They are designed to test students' knowledge of different data presentation methods and their ability to choose the right technique for various datasets. By practicing these questions, students can assess their understanding, identify areas for improvement, and gain confidence in their ability to apply these skills in real-world situations.
NCERT Class 11 Economics Chapter 4
NCERT Class 11 Economics Chapter 4 is dedicated to the presentation of data, a foundational aspect of the economics curriculum. This chapter provides a thorough introduction to the various methods of presenting data, emphasizing their relevance in economic analysis. It discusses the significance of accurately representing data to understand economic trends and patterns.
The chapter is crucial for students to develop a strong base in economics, as it lays the groundwork for more advanced topics in the subject. Understanding this chapter is key for students to excel in their economic studies and develop skills essential for future academic and professional endeavors.
- Presentation of data class 11:
- All CBSE notes
- All ECONOMICS notes
- All 11 COMMERCE notes
You may like these also

The Tiny Teacher Question Answers

Chitthiyon Mein Europe Question Answer

Fractions Class 6 Extra Questions With Answers & Mind map
Heat Class 7 Notes, Mind map & Revision Questions
Teaching resources, test generator, worksheet generator, elearning for students, practice question paper, mock test series, happy parenting, elearning for child, worksheet for child, mock test series for child, witknowlearn, privacy policy, terms and condition, refund/cancellation policy.

Or login with Google
Notification
Upgrade to better learning opportunities.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Sandeep Garg Economics Class 11 Solutions for Chapter 3

Class 11 Economics Sandeep Garg Solutions Chapter 3 – Diagrammatic Presentation
Sandeep Garg Class 11 Economics Solutions Chapter 3 is an illustration curated by professional economic educators for students to comprehend the concepts and procure good scores. The Sandeep Garg Solution is a credible source of reference that provides fundamentals and a comprehensive understanding of solved exercises for economic students. The Solutions offer an enhanced preparation process, and students can download the chapter-wise solutions from here for free and prepare accordingly.
The professional economic educator illustrated the diagrammatic presentation from Sandeep Garg Economics Class 11 textbook solutions chapter 2 from the contemporary edition of the textbook. Students can learn more about the subject through Sandeep Garg Economics Class 11 Solutions. As students complete their homework or study for their exams, these insights will be a valuable asset. Economics is a subject with numerous concepts, but here we present the solution from our Tabular Presentation, which will be quite helpful to the students who are preparing for their exam.
Sandeep Garg Economics Class 11 Solutions for Chapter 3 – Diagrammatic Presentation
Introduction to class 11 economics sandeep garg solution chapter 3 pdf.
The Sandeep Garg Class 11 Economics Solutions Chapter 3 is an easy and scoring chapter that presents how to show data efficiently through the use of diagrammatic presentations like bar charts, histograms, pie charts, and so on.
The Sandeep Garg Class 11 Economics Solutions Chapter 3 is the study of data in a simple and presentable manner through the representation of diagrams.
There are Two Basic Types of Diagrammatic Presentations
1. Geometric Form: The Geometric type of diagrammatic presentation includes presentations like- Pie Diagram and Bar Diagram
Circular or Pie Chart
There are radii at each corner of the circle to divide the area into sectors, so a pie chart consists of a circle. Further, the sector values are proportional to those of the items that are under investigation. Additionally, the circle comprises the entire data set under consideration.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Drawing Pie Charts
Provide a percentage breakdown of the components of the data given
In the center of the circle, the angle is 360 degrees, so divide each percentage component by 3.6.
Make a circle.
Divide the circle into sectors according to the central angles of each percent component.
Use different shades for each sector.
2. Frequency Diagram: The Frequency type of diagrammatic presentation includes presentations like- Histogram, Frequency Polygon, Frequency Curve, and Ogive curve. Line charts or polygons showing frequency distributions are called frequency diagrams. Below is a frequency chart showing the corresponding table results. The midpoint of each group represents the frequency polygon of grouped data.
Histograms are bar graphs that show frequency distributions. Follow the below mentioned important steps on how to create a histogram:
Place frequencies are displayed vertically. The frequency axis in this place would be labeled as the term "Frequency.".
Place each interval's lower value on the horizontal axis. Provide a label for this axis explaining what data are shown (the price of birthday cards, etc.).
In each interval, make a line extending from the smallest value to the smallest value of the next interval. It is recommended that each bar have the same height as the frequency of the interval it represents.
Advantages of Diagrammatic Presentation
The use of diagrammatic presentation in a chapter helps in a better understanding of the concept. Given below are some of the advantages of it:
The Class 11 Economics Diagrammatic Presentation Sandeep Garg chapter presents data in the form of a simple and colorful manner appealing and at the same time in a comprehensive manner.
The Diagrammatic Presentation in a chapter saves a lot of time as it presents complex data in a simplified manner.
Diagrammatic Presentation Class 11 Economics Sandeep Garg chapters are more informative as they not only depict data characteristics but also reveal other hidden relations and facts which remain unsolvable from the classified and tabulated data.
The Diagrammatic Presentations are super easy to comprehend as they give a great memorizing effect.
Class 11 Economics Sandeep Garg Solution Chapter 3 Pdf helps students present a huge mass of complex data in an intelligible, simplified, and understandable form
The Diagrammatic Presentation chapter presents two sets of data in a visually pleasing and easily comparable manner.
The diagrammatic representation of data is easy to understand by a common man. Diagrams are really too attractive and they are also impressive, with many newspapers and magazines using them often so that they can describe certain phenomena. Advertisement campaigns also utilize diagrams heavily nowadays.
Simplified Presentation-You can easily present large volumes of complex data in a simplified and understandable way by using diagrams.
A hidden fact is revealed when data is sorted and tabulated - some facts are not revealed during this process. Data visualization helps reveal these concealed facts as well as their relations.
Diagrams help people to grasp the data easily when it is presented in a graphical form.
Compare with ease - Diagrams make it easy for people to compare data.
This is universal - almost all fields of study such as business, economics, social institutions, administrative work, etc. make use of diagrams. Consequently, they are universally accepted.
A General Principle of Diagrammatic Presentation of Data
In order to best communicate the information contained in statistical data, a diagrammatic presentation is the best method. In order to make diagrammatic presentations more effective tools for understanding data, you should follow the following general principles:
The title should give a clear, concise, and unambiguous explanation of the topic. In the footnote below the diagram, you can provide more information about the title.
Diagrams must be constructed so that the viewer is immediately engaged. Your drawing should be drawn neatly, with an appropriate balance between its length and breadth. Also, you have to make sure about the fact that the diagram is neither too large nor too small. Colors, shades, and sizes can also be used to emphasize different aspects of a problem.
Ensure that the drawing is accurate by using the proper measurements and colors. Always put accuracy above attractiveness in your drawings.
Consider the nature of the data and the purpose of the investigation when selecting the design of the diagram.
The diagram should be indexed if you use different shades or colors to illustrate different characteristics.
Please specify where the data comes from if you are using a secondary source.
Your diagram should be as simple as possible.
Preparation Tips
The Class 11 Economics presents theories in Tabular or Graphical or Diagramatic presentation along with the necessary formula for students to comprehend readily.
Students should ensure to practice the problems that involve diagrammatic presentations regularly.
The most effective preparation approach is to understand the working and application of a formula over memorizing. A thorough understanding and regular practice of all the important formulas chapter-wise helps better comprehension of the chapter.
Students must comprehend and analyze the logic and reasoning of all the important topics and give special focus to the various graphical presentations.
The Sandeep Garg Class 11 Solutions for Economics Chapter 3- Diagrammatic Presentation is a chapter that presents a comprehensive view of all the important concepts and problems important for students during preparation or revision for the exam. The Class 11 Sandeep G arg Solution Diagrammatic Presentation helps students enhance and better their preparation and change their score game.

FAQs on Sandeep Garg Economics Class 11 Solutions for Chapter 3
1. How does diagrammatic data presentation differ from other methods?
Diagrams are geometrical figures such as lines, bars, circles, squares, etc., which help present data in a manner that is more intuitive. A diagrammatic presentation of data offers the following advantages:
Easy to understand- Graphs facilitate the understanding of data because they are attractive, impressive, and they are used frequently in newspapers and magazines to illustrate certain facts or phenomena. Modern advertising campaigns also use diagrams.
Simplified Presentation- Using diagrams, you can represent large amounts of complex data in a simple and understandable way.
Reveals Hidden Facts- During the classification and tabulation of data, some facts are hidden. Visualizing data using diagrams helps reveal these facts, as well as their relationships.
2. How to prepare for Class 11 Economics Chapter 3 – Diagrammatic Presentation?
You can prepare for Class 11 Economics Chapter 3- Diagrammatic presentation in the following ways-
Understanding the detailed topic that was explained should be the first and most important if you are preparing for a Diagrammatic presentation.
Diagrams tend to be easy if you search for the relevant information given in the question only. Different study pie charts and other histograms as well give you a detailed version of the answer.
Always make notes of the important topics with their graphical presentation only as it will help you in learning those concepts in an easier way.
After completing your syllabus, test your preparation by solving sample papers. You can download a free PDF of sample papers and solutions from Vedantu’s website or mobile app.
3. How pie charts can be helpful for a diagrammatic presentation?
Pie charts can be helpful for a diagrammatic presentation in the following ways.
The pie chart gives you a chart view of the numbers and other important topics which are mentioned in the questions.
Pie chart provides you with a circle representation of your answer about how much percentage that topics hold and how the answer is divided with the diagrammatic view.
A pie chart is best used when trying to work out the composition of something. If you have categorical data then using a pie chart would work really well as each slice can represent a different category.
4. What are the key areas in Diagrammatic Presentation you must focus on before Class 11 Economics Exams?
The key areas including Diagrammatic presentation you should focus on before you are going for Class 11 Economics exams are-
Make sure you have practised pie charts, histograms, frequency graphs enough so that you can understand the concept of the graphs
Always make a picture in your mind whenever you are attempting any question so that you can have an idea about how the charts should be done
Make sure to practice sample papers as much as possible to understand the level of questions that can be there in your exams.
5. What is the importance of diagrammatic presentation?
An easy-to-follow diagram is easy to comprehend. A simplified representation can simplify a large amount of data. Data can be presented in a simple and effective way by using diagrams. You can represent large quantities of complex data in a way that makes sense. A simple and effective tool for presenting the information that any statistical data contains. Diagrams are usually attractive and impressive, and newspapers and magazines use them frequently to explain certain phenomena and facts related to data.
- Diagrammatic Presentation of Data
Nowadays a lot of emphases is laid upon exceptional presentation of data. All of this is because, when presented diagrammatically, data is easy to interpret with just a glance. In such a case we need to learn how to represent data diagrammatically via bar diagrams, pie charts etc.
Suggested Videos
Bar diagrams.
As the name suggests, when data is presented in form of bars or rectangles , it is termed to be a bar diagram.
Features of a Bar
- The rectangular box in a bar diagram is known as a bar. It represents the value of a variable .
- These bars can be either vertically or horizontally arranged.
- Bars are equidistant from each other.
- Each bar originates from a common baseline or a common axis.
- The width of bars remain same but the height changes, according to the value of a variable, to denote the difference between their values.
- Unless they are in a specific order, the convention is that bars can be arranged in an ascending or descending order.
Browse more Topics under Presentation Of Data
- Textual and Tabular Presentation of Data
Types of Bar Diagrams
Simple bar diagram.
These are the most basic type of bar diagrams. A simple bar diagram represents only a single set of numerical data. Generally, simple bar diagrams are used to represent time series data for a single entity.
Generally, the Y-axis contains markings which represent the range of the value of variable whereas the X-axis contains divisions for entities like years, time periods, areas etc.
Multiple Bar Diagram
Unlike single bar diagram, a multiple bar diagram can represent two or more sets of numerical data on the same bar diagram. Generally, these are constructed to facilitate comparison between two entities like average height and average weight, birth rates and death rates etc.
Separate sets of numerical data are differentiated with the help of colour variation. By the same token of simple bar diagrams, multiple bar diagrams also have divisions on Y-axis and X-axis that represent different values of the variable and entities like year, areas etc. respectively. Note that each division on X-axis has two or more bar diagrams each according to the specified number of bars.
Sub-divided or Differential Bar Diagrams
Sub-divided bar diagrams are useful when we need to represent the total values and the contribution of various sections of the total simultaneously. The different sections are shaded with different colours in the same bar.
For example, such a bar diagram can be used to represent the varying levels of employment over the years in India and each bar can be divided into two sectors, the urban and rural. Again, here the Y-axis and X-axis represent same values as in simple and multiple bar diagrams.
Percentage Bar Diagrams
This is derived further from the subdivided bar diagrams. In this, each bar has the same height that represents 100 percent of the Y-axis in totality. Further, each bar is divided into sections based on percentages calculated according to the contribution of these sections.
Percentage bar diagrams are used when the values are really high. This is because using subdivided bar diagrams in such cases would not be easy and appropriate.
Deviation Bar Diagrams
Lastly, the deviation bar diagrams are most interesting of the lot. In such a type of bar diagram, there are both negative and positive values on the y-axis. The deviation bar diagrams are used to compare the net deviation of related variables with respect to time and location.
For example, it can be used to represent a bar diagram for savings (represented by positive deviations) and deficit (represented by negative deviations) over years.

Pie or Circular Diagrams
In addition to bar diagrams, pie diagrams are also widely used to pictorially represent data. In this, a circle is divided into various segments which are decided on the basis of percentages. Which means the circle is divided into sectors depending on various percentages.
These sectors are differentiated with the help of colours. Pie diagrams have an edge over bar diagrams because they can easily provide an overview and provides a better sense of contributions of each part. The steps for construction of a pie diagram are:
The first step involves finding out respective percentages. This is done by a simple mathematical formula to find out percentages which is –
{(Parts for the respective sector)/total parts) ×100} .
For example, if in a class of 1oo students, 30 are obese, 20 are fat and 50 are slim then the percentages will be as follows:
(30/100) × 100= 30%
(20/100) × 100= 20%
(50/100) × 100= 50%
2] A circle comprises 360 degrees. The angles that each sector will span across is decided by the given formula: (Percentage value/100)×360°
3] Finally, just plot these values according to their respective angles on a circle and give appropriate markings to complete the pie chart.
A Solved Example for You
Q: Which among the following is not a feature of a bar in the bar diagram?
- The width is same but the heights are generally different
- They are rectangular in shape
- Bars should not be equidistant
- Each bar originates from a common baseline
Ans: Of all the above options, option C is incorrect because conventionally the bars should be equidistant.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Presentation of Data
- Textual And Tabular Presentation Of Data
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- Class 11 Commerce
- Sandeep Garg Solutions Class 11 Economics
- Chapter 3 Diagrammatic Presentation
Sandeep Garg Solutions Class 11 Economics Chapter 3 Diagrammatic Presentation
Sandeep Garg Class 11 Economics Solutions Chapter 3 Diagrammatic Presentation is illustrated by the professional economic educators from the contemporary edition of Sandeep Garg Economics Class 11 textbook solutions.
We at BYJU’S provide Sandeep Garg Economics Class 11 Solutions to give a comprehensive insight into the subject. These insights will be a valuable advantage to students while completing their homework or while studying for their exams.
Here are some questions along with their solutions from the topic of the Diagrammatic presentation.
Download PDF of Sandeep Garg Economics Class 11 Solutions Chapter 3 Diagrammatic Presentation

The above-provided solutions are considered to be the best solution for ‘Sandeep Garg Economics Class 11 Solutions Chapter 3: Diagrammatic Presentation. Stay tuned to BYJU’S to learn more.
| COMMERCE Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The different forms of presentation of data are: (i) Textual and descriptive presentation (ii) Tabular presentation (iii) Diagrammatic presentation Stay tuned to BYJU'S for more CBSE Class 11 Statistics important questions, question papers, sample papers, syllabus, and Commerce notifications.
Question 4. Data represented through arithmetic line graph help in understanding. (a) long term trend. (b) cyclicity in data. (c) seasonality in data. (d) All of the above. Answer: (a) Arithmetic line graph helps in understanding the trend, periodicity, etc in a long term time series data. Question 5.
The "Important Questions : Presentation of Data Class 11 Questions" guide is a valuable resource for all aspiring students preparing for the Class 11 exam. It focuses on providing a wide range of practice questions to help students gauge their understanding of the exam topics.
Presentation of Data MCQ for Class 11: Get here Collection of Data Multiple Choice Questions and Answers, Download the free PDF of CBSE Class 11 Economics, Chapter 4 of Statistics for Economics.
In this video CA Parag Gupta Sir (RKG Institute) will be discussing all types of diagrams in the chapter Diagrammatic presentation of data.Hope you like the ...
Class XI Statistics Presentation of Data CBSE Worksheet www.vedantu.com 3 14.Out of a total number of 1750 people, who applied for a job, 1150 were females. Out of total applicants, 1420 were graduates and others were post graduates. The number of male applicants who were post graduates were 250.
NCERT solutions for Mathematics Class 11 Economics (Statistics for Economics) CBSE 4 (Presentation of Data) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Revision Notes. Chapter - 4. Presentation of Data class 11 Notes Economics. The presentation of data means exhibition of data in such a clear and attractive manner that these can be easily understood and analysed. Forms of Presentation of data: 1. Textual/Descriptive Presentation. 2. Tabular Presentation.
T.R. Jain and V.K. Ohri Solutions for Class 11 Statistics Economics Chapter 6 - Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams and Pies Diagrams, covers all the questions provided in T.R. Jain and V.K. Ohri Books for 11th Class Statistics for Economics Subject. At BYJU'S, it is available for free download here.
Statistics for Economics Class 11 Notes Chapter 4 Presentation of Data. Textual Presentation In textual presentation, data are a part of the text of study or a part of the description of the subject matter of study. Tabular Presentation of Data "Tabulation involves the orderly and systematic presentation of numerical data in a form designed ...
Accordingly, it becomes easy to remember the statistical facts. (5) Economical: Tabular presentation is a very economical mode of data presentation. It saves time as well as space. Please refer to Presentation of Data Class 11 Statistics notes and questions with solutions below.
Presentation of data class 11 exercise consists of a range of questions, from simple ones that test basic understanding to more complicated questions that require higher-order thinking. These exercises are designed to provide practical experience in both interpreting and presenting data. The questions often come in various formats, including ...
Can Analyse Solutions: Students can easily match the given answers after attempting questions of Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams & Pies Diagrams with the help of solutions provided in the TR Jain class 11 PDF Solutions, this is considered to be the major impact in the preparation level. Can Improvise Concentration: Concentration ...
Concept of Diagrammatic Presentation. It is a technique of presenting numeric data through pictograms, cartograms, bar diagrams, and pie diagrams. It is the most attractive and appealing way to represent statistical data. Diagrams help in visual comparison and they have a bird's eye view. Under pictograms, we use pictures to present data.
T.R. Jain and V.K. Ohri- Statistics for Economics Solutions for Class 11-commerce Statistics for Economics CBSE Chapter 6: Get free access to Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams and Pies Diagrams Class 11-commerce Solutions which includes all the exercises with solved solutions. Visit TopperLearning now!
For students looking for an in-depth understanding of diagrammatic presentation, our Diagrammatic Presentation of Data Class 11 Notes are just what you need. These notes provide detailed insights into different types of diagrams and how they can be used to represent data effectively. ... Presentation of Data Class 11 Extra Questions Answers. To ...
Class 11 Economics Sandeep Garg Solution Chapter 3 Pdf helps students present a huge mass of complex data in an intelligible, simplified, and understandable form. The Diagrammatic Presentation chapter presents two sets of data in a visually pleasing and easily comparable manner. The diagrammatic representation of data is easy to understand by a ...
Bar Diagrams. As the name suggests, when data is presented in form of bars or rectangles, it is termed to be a bar diagram. Features of a Bar. The rectangular box in a bar diagram is known as a bar. It represents the value of a variable. These bars can be either vertically or horizontally arranged. Bars are equidistant from each other.
Sandeep Garg Class 11 Economics Solutions Chapter 3 Diagrammatic Presentation is illustrated by the professional economic educators from the contemporary edition of Sandeep Garg Economics Class 11 textbook solutions.. We at BYJU'S provide Sandeep Garg Economics Class 11 Solutions to give a comprehensive insight into the subject. These insights will be a valuable advantage to students while ...