
- My presentations

Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Generations of computer
Published by Valentine Harris Modified over 6 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Generations of computer"— Presentation transcript:

HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT By: Pratama Wahyu Purnama ( ) Maulida Yulianti ( )

1 Maninder Kaur
History of Computing -- Soujanya. Contents Definition Abacus(600 B.C) Cardboard Calculator First Calculator Difference Engine(1822) Well-Known Early Computers.

Chapter Chapter Goals Describe the layers of a computer system Describe the concept of abstraction and its relationship to computing Describe.

Chapter 1 An Overview of Personal Computers

CS 104 Introduction to Computer Science and Graphics Problems History of Computer 09/05/2008 Yang Song (Prepared by Yang Song and Suresh Solaimuthu)

The History of Computers By: Casey Walsh. Introduction Computer history can be broken down into five generations of change. Computer history can be broken.

Prepared by: Jasper Francisco. The Early Years 1 In the early years, before the computer was invented, there were several inventions of counting machine.

COMPUTER SYSTEM.

Chapter 01 Nell Dale & John Lewis.

INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING. Computer Evolution History of Computers Generations of Computer First Generation Second Generation Third Generation.

Generational Computing CSCI 1060 Fall CSCI 1060 — Fall 2006 — 2 First Generation Large computers, difficult to program Primarily used by scientists.
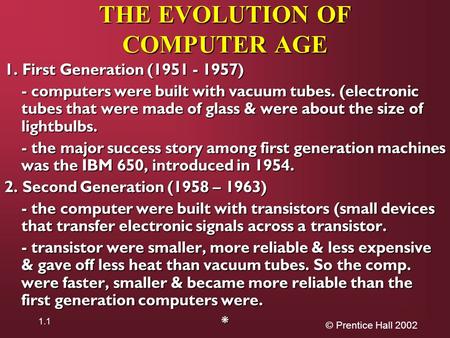
© Prentice Hall THE EVOLUTION OF COMPUTER AGE 1. First Generation ( ) - computers were built with vacuum tubes. (electronic tubes that.

Chapter 1 The Big Picture.
Generations Of Computer Copyright(c)2011 Presentation Point( om)

Information Technology

Computer Science What is Computer Science? Algorithm Design and Analysis Organization and Architecture Artificial Intelligence Databases Operating Systems.

Generation of Computers

COMPUTER GENERATIONS STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT. FIRST GENERATION 1940 – 1956 VACUUM TUBES USE VACUUM TUBES FOR CIRCUITS USE MAGNETIC DRUMS FOR MEMORY – DATA.

Computer Generations ITSC 1401, Intro to Computers Instructor: Glenda H. Easter.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
GENERATIONS OF COMPUTERS
Nov 19, 2014
280 likes | 881 Views
GENERATIONS OF COMPUTERS. FIRST GENERATION 1951 - 1959. Use of vacuum tubes as a means of storing data in the memory. Made the use of punched cards obsolete Computer boards were replaced by computer program Storage capacity of 100 bytes to 2 kilobytes (2,000 bytes)
Share Presentation
- generation computers
- output devices
- storage capacity
- fourth generation computers
- improved secondary storage devices

Presentation Transcript
FIRST GENERATION 1951 - 1959 • Use of vacuum tubes as a means of storing • data in the memory. • Made the use of punched cards obsolete • Computer boards were replaced by computer • program • Storage capacity of 100 bytes to 2 kilobytes • (2,000 bytes) • Can perform 2,000 to 16,000 addition • per second
SECOND GENERATION 1959 - 1964 • Use transistors and diodes • Computers are smaller in size, faster, more reliable • and much greater in processing capacity • Has built-in error detecting device • Printers were developed • Storage capacity of 6 KB to 1.3 MB • Can process up to 6,000 to 3M operations per • second TRANSISTORS • made of silicon • forty times faster than vacuum tubes
THIRD GENERATION COMPUTERS 1965 - 1970 • Integrated solid circuitry was developed • Improved secondary storage devices • New input and output devices was developed • Increased speed of about 10,000 by means of IC’s • Multitasking • Can perform 100,000 to 400M operations per second INTEGRATED CIRCUITS • Has many transistors in one silicon • Developed by Jack St. Claire Kilby in 1958 • First IC was invented in 1961 • Also known as the “silicon ship”
FOURTH GENERATION COMPUTERS 1970 - present • Development of microelectronics • Multiprocessing, multiprogramming, time sharing, • Multitasking miniaturization, operating speed, • and virtual storage • Can do more than one function • Its size was of the television or smaller • It can do 500, 000 to 1B operations per second MICROPOCESSOR • Less than 1 inch square and can contain millions of • electronic circuits • A complete computer on a chip • Can input, process and output
FIFTH GENERATION COMPUTERS Present and beyond Artificial Intelligence • Devices are based on artificial • intelligence and are still in development • Includes voice recognition • Goal is to develop devices that respond • to natural language input and are capable • of learning and self - organization
- More by User

Generations of wireless networks
Generations of wireless networks. Chapter 1. 1G wireless standards. 2G wireless. 3G wireless. 4G wireless. Where is wireless access going???. Many (maybe too many) wireless technology choices are available today Short-range (WLAN’s, sensor technologies such as Bluetooth or Ultra Wideband)
1.58k views • 27 slides

Generations
Generations. Cycles in American Life Cary Matsuoka. Introduction. First heard this topic in January 2007 Superintendents conference Speaker - William Strauss Historian, playwright, lawyer Passed away in December 2007, age 60 Co-writer, Neil Howe Historian, demographer, economist.
659 views • 37 slides

GENERATIONS
GENERATIONS. Neil Howe and William Strauss. G. I. 1901 – 1924 John F. Kennedy Clare Booth Luce. SILENT 1923 – 1942 Colin Powell Gloria Steinem. BABY BOOMERS 1943 – 1960 David Spielberg Oprah Winfrey. GEN X 1961 – 1981 Michael Jordan Jodie Foster. MILLENNIALS 1982 – 2002
240 views • 17 slides

Generations. HUM 2051: Civilization I Fall 2012 Dr. Perdigao August 29, 2012. Recycling Dates. 2000-1700 BC/BCE Age of Patriarchs: Abraham, Isaac, Joseph 1700-1500 BCE Hebrews prosper in Egypt under Hyksos
248 views • 7 slides
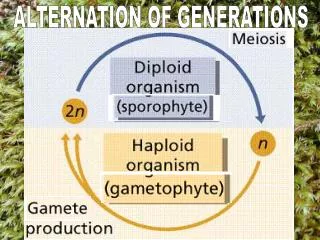
ALTERNATION OF GENERATIONS
ALTERNATION OF GENERATIONS. SINGLE COMPLETE MOSS PLANT. SPOROPHYTE. CAPSULE. GAMETOPHYTE. RHIZOIDS. NOTICE THE CAPSULES ON THE SPOROPHYTE STALKS. STALKS ARE NEEDED TO GET THE CAPSULE OUT OF THE MOIST GREEN MOSS MAT. QUIZ YOURSELF. WHAT ARE THESE PARTS OF A SINGLE MOSS PLANT?.
295 views • 11 slides

Generations of Faith
Generations of Faith. Lifelong faith Formation for The Whole Parish Community. Foundations of Generations of Faith. Foundation 1: A Living Faith Foundation 2: A Lifelong Learning Community Foundation 3: A comprehensive Framework Foundation 4: A Model of Catechizing Activity.
678 views • 25 slides

Generations. An Overview of Generational Behavior, Attitudes, and Leadership. The Open Classroom Spring 2010. Familial Generation. Average time between a mother’s first offspring and her daughter’s first offspring U.S. (2007) 25.2 years U.K. (2004) 27.4 years. Cultural Generation.
790 views • 22 slides

Generations of Ipod
Generations of Ipod. By: Sean Caldwell & Daren McNeese. Classic IPod . The iPod was created by the apple company, and started out as a regular mp3 player. With the first generation made in 2001. It could hold at least 1000 songs on its 1.8” hard drive.
261 views • 10 slides

In the Workplace. GENERATIONS. Lorelei Penera May 10, 2012. Agenda. Characteristics of Generations Tips to working with each generation Public Sector Problem Recommendations Questions. Working Generations. Traditionalists/Veterans- “Loyalists”. Influences Great Depression World Wars
425 views • 12 slides
Generations.
150 views • 2 slides

Generations of Computer
Generations of Computer. Generations of Computer. The computer has evolved from a large-sized simple calculating machine to a smaller but much more powerful machine. The evolution of computer to the current state is defined in terms of the generations of computer.
2.54k views • 29 slides
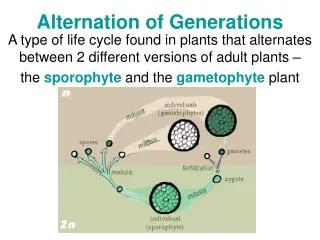
Alternation of Generations
Alternation of Generations. A type of life cycle found in plants that alternates between 2 different versions of adult plants – the sporophyte and the gametophyte plant.
2.11k views • 5 slides

GENERATIONS. Presented By Brad Nesheim Brian Stuver. A group of people born in the same time frame with common cultures and attitudes. What is a Generation?. Zits Comic Strip. BSA is 100 years old Think about the last 30 years. How is it the same? How is it different?.
416 views • 26 slides

Generations. HUM 2051: Civilization I Fall 2014 Dr. Perdigao August 25-27, 2014. Recycling Dates. 2000-1700 BC/BCE Age of Patriarchs: Abraham, Isaac, Joseph 1700-1500 BCE Hebrews prosper in Egypt under Hyksos
158 views • 7 slides

The Five Generations of Computers
The Five Generations of Computers. First generation computers (1940-1956). The first computers used vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for memory. They were often enormous and taking up entire room. First generation computers relied on machine language.
10.41k views • 11 slides

The Five Generations of Computers. INTRODUCTION
935 views • 12 slides

Generations. The role of Millennials, GenX, Boomers, Silents and Plurals in society and culture Dr. Pete Markiewicz Indiespace/Lifecourse Associates [email protected]. Topics. What are generations? Cohort effects Defining generations Generational models Generation Me GenY
950 views • 59 slides

GENERATIONS. Ms. Michelle White and Mr. Justin Douglas. Learning Objectives. Recognize : The importance of developing and maintaining inclusive relationships for all generations Identify : Generational profiles, experiences, and influences
377 views • 32 slides

different generations of computers.
qincludes introduction ,points on different generation of computers and its advantages and diadvantages.
488 views • 13 slides

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Mar 24, 2017 · This presentation provides an overview of computer generations from the first to fifth generation. It discusses the key developments and technologies that define each generation, including vacuum tubes, transistors, integrated circuits, microprocessors, and artificial intelligence.
Nov 19, 2014 · The second generation introduced transistors, making computers smaller and more efficient. The third generation used integrated circuits and silicon chips, allowing for interaction through keyboards and monitors. The fourth generation began using microprocessors, leading to the development of personal computers and networks.
Aug 24, 2012 · 5. Fourth Generation Computers Time Period : 1975 to Today Technology : VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) Incorporated many millions of transistors & electronic circuits on a single chip Size : Small as compared to first generation computer Processing : Faster then first generation computer Characterized by: The personal computer and user friendly micro-programs, very fast processor chip ...
Generations of Computer The computer has evolved from a large-sized simple calculating machine to a smaller but much more powerful machine. The evolution of computer to the current state is defined in terms of the generations of computer. Each generation of computer is designed based on a new technological development, resulting in better, cheaper and smaller computers that are more powerful ...
Third generation computers; urth generation compu ers (1971-present) The microprocessor brought the fourth generation of computers, as thousands of integrated circuits were built onto a single silicon chip. The Intel 4004 chip, developed in 1971, located all the components of the computer. From the central processing unit and memory to input ...
* Generations of Computer Currently, there are five generations of computer. In the following subsections, we will discuss the generations of computer in terms of the technology used by them (hardware and software), computing characteristics (speed, i.e., number of instructions executed per second), physical appearance, and their applications.
Computer Generations Generation in computer terminology is a change in technology a computer is/was being used. Initially, the generation term was used to distinguish between varying hardware technologies. But nowadays, generation includes both hardware and software, which together make up an entire computer system. There are totally five computer generations known till date. Each generation ...
Dec 19, 2019 · The Five Generations of Computers. The Five Generations of Computers. First generation computers (1940-1956). The first computers used vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for memory. They were often enormous and taking up entire room. First generation computers relied on machine language. 10.4k views • 11 slides
Nov 19, 2014 · The Five Generations of Computers. The Five Generations of Computers. First generation computers (1940-1956). The first computers used vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for memory. They were often enormous and taking up entire room. First generation computers relied on machine language. 10.41k views • 11 slides
Jan 15, 2014 · The document discusses the five generations of computers from the first generation in 1946 to the present fifth generation. The first generation used vacuum tubes and were large, heat-producing machines. The second generation introduced transistors, reducing size and heat. The third generation used integrated circuits which further reduced size.